Test For Unsaturation in Organic Compound
In an organic compound, unsaturation is due to the presence of double (>C=C<) or triple (–C≡C–) bonds in the molecule. The presence of unsaturation is tested by the following two methods:
- Bromine water test
- Baeyer's test (using 1% alkaline potassium permanganate solution)
Bromine Water Test
The organic compound is treated with bromine water drop wise. The decolourisation of bromine water shows the presence of unsaturation in the organic compound.
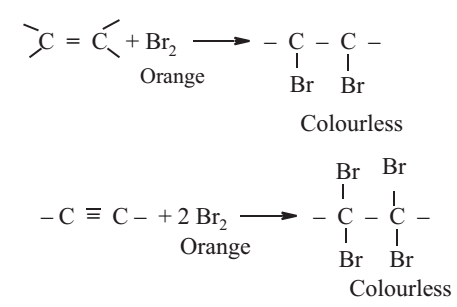
Baeyer's Test
The organic compound is treated with an aqueous solution of alkaline potassium permanganate (Baeyer's reagent). The disappearance of the pink colour of potassium permanganate shows the presence of unsaturation.
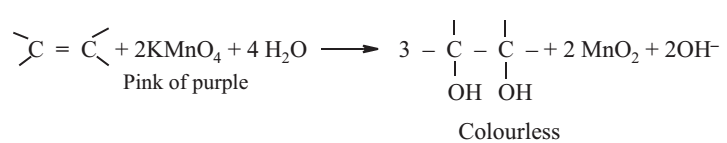
How To Perform Experiment
Bromine Water Test
To a solution of 0.2 g of the organic compound in water or CCl4, add bromine water or bromine in CCl4 drop wise. Shake the mixture after each addition.
Baeyer's Test
To the organic compound (0.5 g) add 1 mL of 0.5% aq. KMnO4 solution drop wise.
Precautions
-
Do not inhale the bromine water or bromine in carbon tetrachloride.
-
If the compound is soluble in water, use bromine water for testing. If the compound is insoluble in water, then dissolved 5 mL of the compound (liquid) or a pinch of the solid in 1 mL of carbon tetrachloride and test it with bromine in carbon tetrachloride solution.
-
Add the reagents drop wise.